At present, the analysis methods of ginsenoside mainly include: colorimetry, thin layer chromatography (thin layer chromatography, TLC) method, thin layer scanning (thin layer chromatography scan, TLCS) method, high performance liquid chromatography (high performance liquid chromatography, HPLC). ) method, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC.MS) method, near-infrared spectrometry (NIRS) method, gas chromatography (gas chromatography, GC) method, rod-shaped thin-layer Scanning method, droplet counter current chromatography (DCCC) method, supercritical fluid chromatography (super. clinical fluid chromatography, SFC) method, ion chromatography - pulsed amperometric detection (ion chromatography with pulsed amperometrie detection, IC.PAD) , micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography, enzyme immunoassay (enzyme immunoassay, EIA), etc. Among these methods, the HPLC method is more widely used because of its characteristics of sensitivity, accuracy, easy operation, and good repeatability. The detection speed is slow and the detection time is long.
While, we use the UPLC (Ultra performance liquid chrimatography) to check the analysis the ginsenosides at various kinds of ginseng extracts powder.
From below picture, we can see:
1, There is Rf peak in ginseng root extract, but there is no Rf in ginseng stem and leaf extract, ginseng fruit extract and American ginseng extract;
2. The fingerprint characteristics of the chromatographic peaks of the stem and leaf extracts are more obvious than those of the root extracts between 6 and 9 minutes in the chromatogram;
3. The Rg1 peak response of red ginseng extract is higher than Re, and the Rg1 peak response of other kinds of extracts is lower than Re.
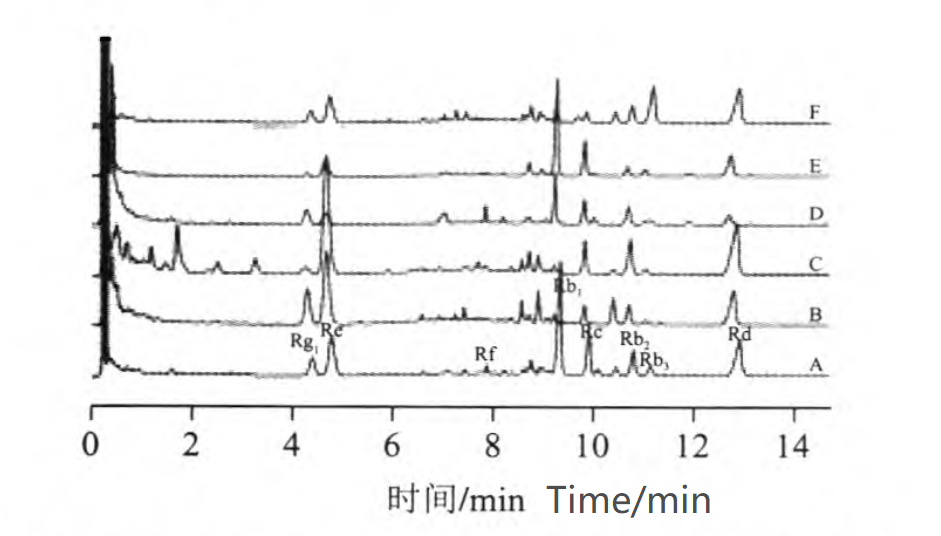
Besides, the Rx/Rg1 or Rx/Re peak area ratio can reflect the characteristics of different kinds of ginseng extracts.
1. From the Rx/Rg1:
a) The ratio of Rb1/Rg1 of ginseng root extract is 3~9;
b) The ratio of Rb1/Rg1 of American ginseng root extract is 14~42;
c) The Rb1/Rg1 ratio of ginseng stems and leaves and American ginseng stems and leaves extracts are mostly less than 1;
d) The values of Rb2/Rg1, Rb3/Rg1, and Rd/Rg1 of ginseng stem and leaf extract are all smaller than those of American ginseng stem and leaf extract.
2. From the Rx/Re:
a) The Rx/Re values of ginseng stem and leaf extracts are all less than 1; and the values of Rb2/Re, Rb3/Re, and Rd/Re of ginseng stem and leaf extracts are also lower than those of American ginseng stem and leaf extracts;
b) Except red ginseng extract, the Rg1/Re of other kinds of ginseng extracts are all less than 1.
From the perspective of a single saponin component:
1. American ginseng root extract has the highest Rb1 content, followed by ginseng root extract;
2. The content of Re in ginseng stems and leaves and American ginseng stems and leaves extract is higher, and the Rb3 content of American ginseng stems and leaves extract is higher than that of ginseng stems and leaves extract;
3. Ginseng fruit extract contains high content of Re, Rd and Rb2;
4. Red ginseng extract basically maintained the characteristics of ginseng extract, but the Rg1 content was higher than Re, which may be caused by the degradation reaction of saponin components during processing.
And, the Ginsenosides can be divided into 3 types according to the structure of their aglycon parts, namely protopanaxadiol (PPD), such as ginsenosides Ra1, Ra2, Rb1, Rb2, Rb3, Rc and Rd; Alcohol-type saponins (protopanaxatriol, PPT), such as ginsenosides Re, Rg1, Rf, Rg2 and Rh1, etc.; oleanolic acid-type saponins, such as ginsenoside Ro.
1. The content of diol-type saponins in ginseng stem and leaf extract and ginseng fruit extract is lower than that of triol-type saponins;
2. Ginseng root extract, American ginseng root extract, American ginseng stem and leaf extract, and red ginseng extract have a higher content of diol-type saponins than triol-type saponins.